16. July 2021
Interview with Niels König I Department Head Production Metrology I Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology IPT about 5G in machine halls
Turning, milling, drilling – Niels König of the IPT clarifies: “We want to introduce 5G into machine halls and their various processes.” The main topic here is the economic efficiency of a business. And that is where 5G and its capabilities play a key role. König: “Every company is continuously looking for ways to keep productivity as high as possible. In doing so, it inevitably faces physical limits, and that’s where 5G offers new opportunities.”
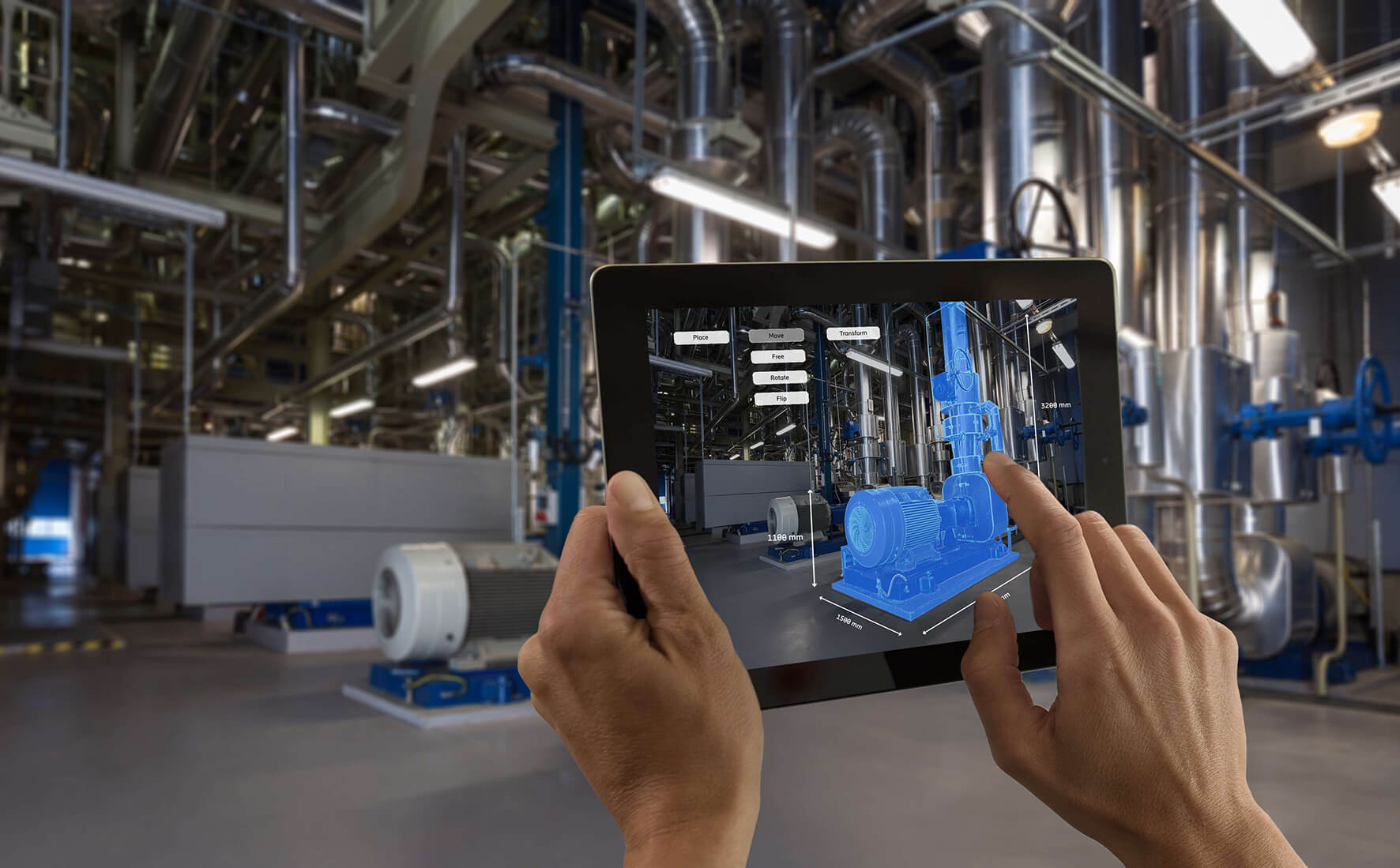
Wireless sensors bring the measurements exactly to the places that, as he puts it, “hurt.” 5G will allow much faster responses than before, for example, before a milling tool breaks. 5G, with latency times in the millisecond range, ensures extremely low response times that were unreachable with other wireless technologies in the past.

Ericsson
Where does research currently stand with 5G? Will we still be in the testing and development phase for a long time or will we soon see it in everyday life? Niels König begins with describing his role: “Applied research is tasked with supporting the technology transfer to the industry. We don’t develop any products. However, we do believe that in collaboration with the industry – and that is exactly what we do – we have a good basis for the development and testing of new products. We have the infrastructure needed for that.” For example, the sensors are developed jointly with providers from the sensor industry. König: “With us, the companies we cooperate with learn how performance could be ideally, and how to go about the technical implementation of 5G.” In the future, companies should be able to develop products on that basis.

Paperplane Productions
5G-based sensor for wireless process monitoring in machining applications
The core challenge is to reliably and safely control and regulate highly dynamic production systems. Therefore, the Fraunhofer IPT is developing a continuous real-time communication infrastructure based on 5G and Time-Sensitive Networking alongside its partners from the areas of mechanical engineering, network technology, and robotics.
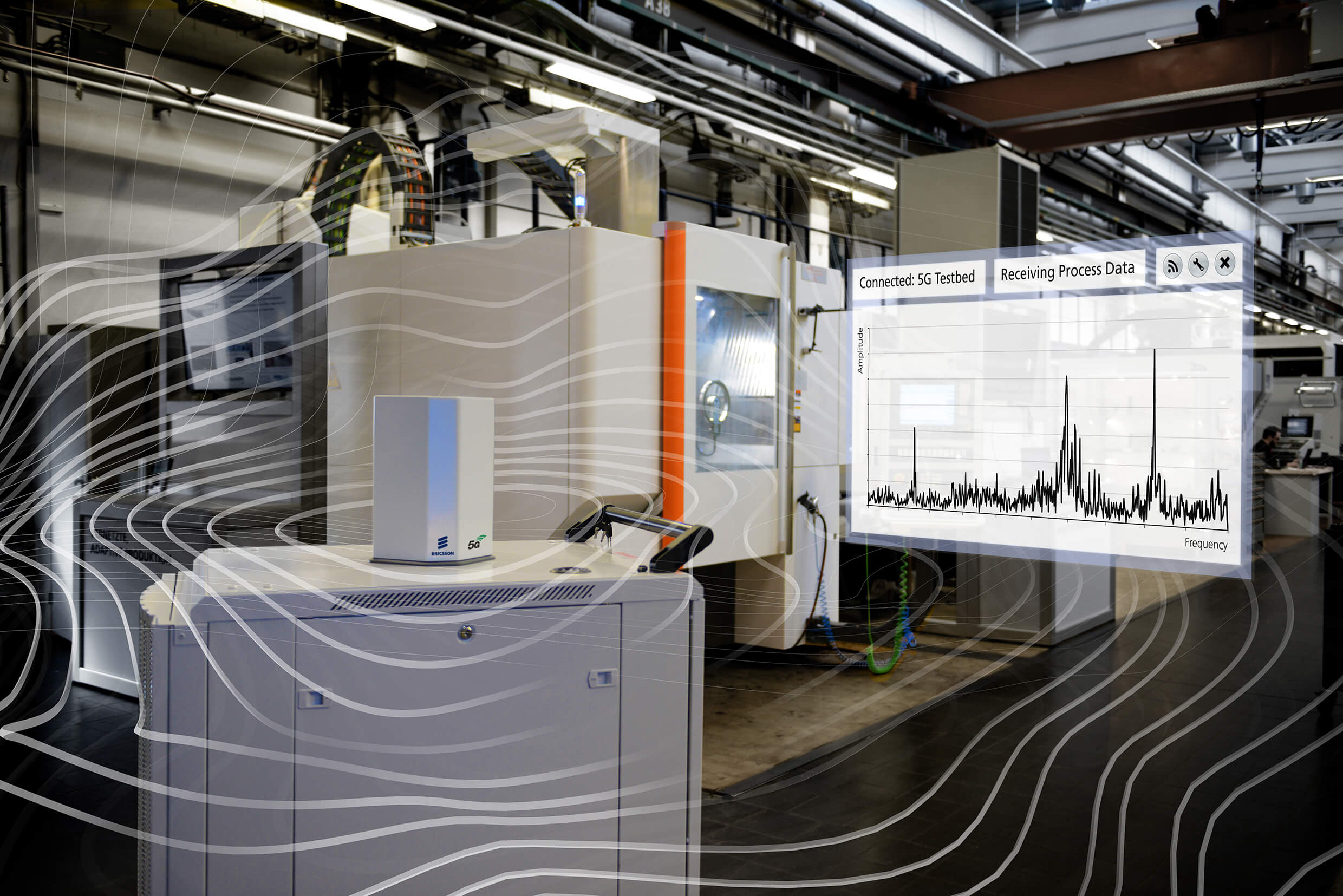
The buzzword here is Edge Cloud, the control center for all connected systems. How does it work? Niels König: The full impact of 5G will be realized, once the enormous amount of data from various sources can be processed, and the latency made possible with 5G will also be made available on the receiving side. Developing a 5G sensor with a latency of one millisecond will have no benefit if the IT infrastructure cannot match the speed. That is why we have a data center just for production. It is called Edge Cloud and is located on-site.” The data from all components in the network merge there. The many individual processes will no longer have to be controlled locally and will be cloud-based instead. All calculations for robotics paths can be done there and the results are returned to the robotics system.

Fraunhofer IPT
In terms of connectivity, there will be a duality: 5G plus cable (copper or fiber optics), says Niels König: “You end up with a completely normal IT communication that is very easily integrated into existing infrastructure. WLAN will be replaced completely and will no longer be needed in the production hall.”
Aachen is excellently positioned with the 5G-Industry Campus Europe, König explains confidently. It is one of the federal government’s model regions, and we are really very, very far ahead. We are intensively involved in various research projects, also on European level. The aim is to introduce the technology into applications. That is our strength.” There are a total of six model regions in Germany.
He is counting on the success of Aachen’s research projects on Campus Melaten. “I know of no other larger project anywhere in the world. Here, we have so many networked indoor and outdoor areas – it is an extremely complex test scenario set up here, which has much more potential beyond its actual function: there is autonomous driving (Institute for Automotive Engineering), for example”. The IPT provides resources for all of that, so that other institutions can also try things out. 5G-COMET, which started at the beginning of this year, is one of six research projects relying on this infrastructure. What we do here is not about more use cases. We are working on the further development of the technology, on realtime and synchronization capabilities.

Ericsson
The 5G research network comprises four indoor networks covering around 7000 square meters in the involved institutes’ machine halls and an outdoor network of one square kilometer. The complexity of the testing possibilities, the cooperation partners on campus and in the industry put Aachen with its 5G-Industry Campus Europe in the leadership position. Bringing together research and industry: 5G with its possibilities is an excellent example. According to Niels König, entirely in line with the campus idea of “hand in hand with the industry.” And names a successful example: One very strong example is Ericsson in Herzogenrath, our partner from the very beginning. Our collaboration is a privilege we have right here in Aachen.”
In seven subprojects, various application scenarios are being examined – from 5G sensor technology for the monitoring and control of highly complex production processes to mobile robotics and logistics to cross-location production chains. Coordinator of the project is Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology IPT, project partners are: Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering (WZL) of RWTH Aachen University, FIR at RWTH Aachen University, IT Center of RWTH Aachen University and Ericsson.
You want to know more about “5G in practical use”?